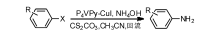作者简介:杨 琴,1987年生,女,硕士,研究方向为有机催化。
C-N偶联反应是合成芳香胺的重要手段,咪唑、脂肪胺和氨常用作该反应的氮源。氨是最简单的氮化合物,应用在该反应中不仅廉价而且更加绿色环保。然而,由于氨结构以及偶联后产物结构使其存在一定的挑战性。各种催化体系的出现实现了以氨为氮源的C-N偶联反应。综述钯和镍在均相、多相体系中催化氨为氮源的C-N偶联合成苯胺类化合物的反应。这类金属催化剂催化活性较高,但存在进一步偶联生成二级胺的问题,且催化剂成本偏高。铜作为廉价金属在C-N偶联反应中的应用一直受到关注,重点介绍各种常见的铜盐、铜纳米材料和负载型铜催化剂等在氨为氮源的C-N偶联反应中的应用。
C-N coupling reaction is an important route for synthesis of aromatic amines.Imidazoles,aliphatic amines and ammonia are usually used as nitrogen sources for the coupling.As the simplest nitrogen compounds,ammonia is of low cost and environmentally-benign for this reaction.But due to the structure of ammonia and the resultant coupling product,using ammonia as nitrogen source is of challenge.Emerging of various catalytic systems makes it feasible C-N coupling reaction using ammonia as nitrogen source.The researches on C-N coupling reaction catalyzed by palladium,nickel and copper in homogeneous and heterogeneous phase,using ammonia as nitrogen source,were reviewed in this paper.These catalytic systems exhibit high catalytic activity,but some systems result in further coupling to form secondary amines byproducts,such as diphenylamines or triphenylamines,and palladium and nickel catalysts are of high cost.As an inexpensive metal,use of copper catalyst in C-N coupling reaction attracts much attention.Application of copper salts,nanoparticle copper and supported copper as the catalysts for C-N reaction using ammonia as nitrogen source was reviewed in detail.
芳香胺类化合物是重要的有机反应中间体, 广泛应用在染料、天然产物、药物中间体和材料化学等领域, 因此, 芳香胺的合成受到关注[1, 2]。卤代芳烃与含氮化合物的C-N偶联是最常见的合成芳香胺化合物的方法[3, 4]。以氨为氮源的C-N偶联反应的研究日益增多, 主要原因有:(1) 氨为最简单的含氮化合物, 廉价易得; (2) 氨为氮源偶联产物为芳香伯胺, 基于氨基的可修饰性强, 偶联产物应用更为广泛。然而, 以氨为氮源合成苯胺的研究也具有一定的挑战性, 主要原因为:(1) 氨是一种配位能力强的配体, 容易与金属络合形成配位化合物, 导致起催化作用的金属失活; (2) 偶联产物苯胺亲核性较强, 且位阻不大, 容易进一步进攻卤代芳烃形成二级芳香胺甚至三级芳香胺; (3) 在一定温度下, 氨容易从溶剂中逸出, 不利于偶联反应的发生[5, 6, 7, 8, 9]。
本文综述各种金属催化体系在氨为氮源的C-N偶联反应中的应用, 包括贵金属钯和镍催化体系, 重点对各种常用的铜催化体系进行详细介绍。
Shen Q等[10]最早报道钯催化氨与卤代芳烃的偶联反应, 以JosiPhos型配体CyPF-t-Bu制备的钯配合物成功催化卤代芳烃和氨偶联生成苯胺。 反应中仍能检测到二级芳胺, 可通过增加底物位阻减少二级胺的生成。该体系中氨为气体状态, 反应要求一定的气体压力, 较高的压力有利于苯胺生成, 因此, 体系对反应设备要求较高, 限制了生产应用。
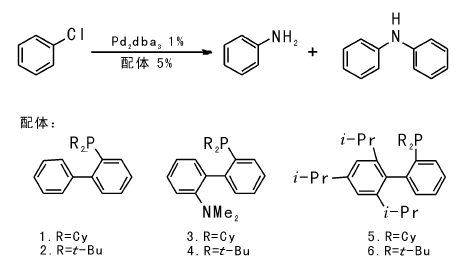
2007年, Surry D S等[11]采用二芳基膦配体和Pd2dba3组成催化体系得到和文献[10]一致的结果。通过调节配体结构, 可选择性实现氨的单芳香化、二芳香化和三芳香化。配体位阻增大或卤代芳烃位阻增大均有利于一级芳胺的生成:
| 表 1 钯催化氨与氯苯偶联 Table 1 Palladium catalyzed the coupling of ammonia and aryl chlorides reported by Buchwald S L |
与文献[10]报道体系比较, 该体系以二氧六环为溶剂, 氨溶于其中, 降低了反应装置耐压性的要求, 有利于催化利用。
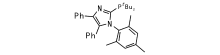
随后, 设计出各种配体用于钯催化氨芳香化反应[12, 13]。2009年, Schulz T 等[14]将一系列含氮杂环膦配体用于钯催化氨芳香化反应中, 芳香底物扩展到惰性的氯代芳烃(图1)。
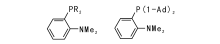
2010年, Lundgren R J 等[15, 16]报道的一系列P, N型配体(图2), 进一步将该类反应底物扩展到各种氯代芳烃, 包括杂环氯代芳烃底物。
这些催化体系虽然高效催化氨芳香化, 但由于钯催化剂价格昂贵, 配体合成也较复杂, 因此, 催化剂的回收和循环使用成为新的研究重点。2016年, Naghipour A 等[17]制备的含膦钯配合物[(CH3C6H4)3PCH2C6H4CH2OC(O)CH3]2[Pd2Br6]以0.3%的低催化剂用量, 在无外加碱和无溶剂的条件下, 也能催化氨水和碘苯甚至溴苯偶联合成苯胺(图3)。该配合物作为多相催化剂, 循环使用4次后, 偶联产率仍达90%。
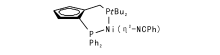
Ni作为Pd同族金属, 常用于催化各种偶联反应。2015年, Borzenko A等[18]报道了镍催化的氨芳基化合成胺反应, 该体系中氮源为氨的二氧六环溶液, 筛选了各种膦配体, 包括常用于钯催化偶联中的BINAP、DPPF、DiPPF和BippyPhos等, 发现这些配体效果均不理想, 而Ni(cod)2配合几种JosiPhos型和一种TaniaPhos型膦配体效果明显(图4)。并以催化效果中等的JosiPhos型膦配体和Ni(cod)2组成的催化体系对芳香型底物进行拓展研究, 10%Ni(cod)2用量能催化各种氯代芳烃、杂环氯代芳烃胺化得伯胺。考虑到Ni(cod)2对空气敏感, 以[NiCl2(dme)]为镍源, 制备出在空气中能稳定保存的镍配合物, 该配合物对氯代杂环芳烃氨基化反应同样有效, 收率达63%。该催化体系拓展了氨芳香化反应的底物范围, 反应中使用氨溶液, 不需要反应装置高耐压性, 推进了该类反应在实际生产中的应用。
Green R A等[19]报道利用苯腈稳定Ni0制备出一种含JosiPhos配体的镍配合物(图5)。该配合物能顺利催化氨(二氧六环溶液)的各种芳香化反应。
以铵盐为氮源, 该反应也能顺利进行。研究发现, 苯腈在稳定Ni0或催化活性物种时起重要作用, 该催化体系将氮源延伸至铵盐, 为实验操作提供了便利。
在催化氨芳香化反应的研究中, 使用更多的金属催化剂为铜催化剂[20, 21, 22], 相对于Pd和Ni, Cu来源更广泛, 价格更低廉。Ullmann F等[23]报道了铜粉催化芳基卤代物的偶联反应, 苛刻的反应条件限制了该反应在实际生产中的应用。随着研究的深入, 开发出各种催化体系用于改善该反应[24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36]。
2001年, Lang F等[25]报道了铜催化氨芳香化反应, 在M3抗体中间体的合成研究中, 首次将铜盐用于催化溴代芳香物合成伯胺。在乙二醇中, 反应温度100 ℃时, Cu2O能催化氨和溴代吡啶化合物偶联得到胺, 产率达91%。该催化体系中存在N原子和O原子之间的亲核竞争, 在各种杂环芳香溴代底物的反应中均检测到醚类副产物, 反应最高选择性可达94%。Lang F等尝试将底物拓展到氯代芳烃, 但该催化体系仅对活化的氯代吡啶(2-氯-5-硝基吡啶)有效果, 未活化的氯代吡啶未检测到对应的芳胺。
Xu H等[26]采用Cu2O为催化剂, 以氨水为氮源, 在H2O和N-甲基吡络烷酮(NMP)的混合溶剂中实现非活化溴代芳烃胺化反应, 采用氨基锂为氮源研究氯代芳烃的胺化, 但得到的主要产物为三苯基胺和二苯基胺。对于铜催化氯代芳烃胺化反应, 将Cu2O-H2O-NMP体系在微波下顺利合成各种氯代芳烃胺化产物(图7)。
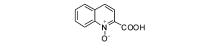
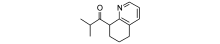
经过几十年的研究, 铜催化氨与卤代芳烃偶联合成苯胺的反应条件越来越温和, 更接近实际生产应用。如2-羧基喹啉氮氧化物(图8)用于CuI催化氨和碘苯偶联, 50 ℃反应12 h, 苯胺收率达93%[27], 但该催化体系对溴代底物需要提高温度和延长反应时间。2008年, Jinho K 等[28]报道的CuI/L-脯氨酸催化体系以K2CO3为碱, 二甲基亚砜为溶剂, 室温下催化碘代芳香化合物与氨的偶联。此外, CuI/L-脯氨酸还能催化氯化铵与碘苯偶联合成苯胺, 对于溴代底物则需要升高温度才能生成对应的苯胺。Xia N等[29]报道的简单配体戊二酮, 配合CuI能有效催化碘代芳烃与氨的偶联。2009年, Wang D等[30]报道2-吡啶-β -酮结构的配体(图9)与CuBr共同作用也能催化碘代芳烃与氨偶联生成苯胺类化合物。
在铜催化氨与卤代芳烃偶联合成苯胺反应中, 一般使用一价铜为催化剂, 如CuI、CuBr、Cu2O等。实际上自然界存在的二价铜多于一价铜, 且较一价铜更为稳定, 更易得到。2010年, Zhu X等[31]以CuO为铜源, 草酰肼为配体, 水为溶剂, 在相转移催化剂的共同作用下, 120 ℃反应0.5 h即实现了溴代芳烃与氨水的高效偶联(图10)。2011年, Li Y等[32]将该体系中酮作为辅助, 室温实现了碘代苯的胺化反应, 但溴代苯与氨水的偶联需要较长的反应时间, 72 h后仍然只能获得中等收率。
2012年, Quan Z等[33]以CuSO4· 5H2O为铜源, 抗坏血酸钠盐原位作用生成Cu+催化实现溴代芳烃与氨水的偶联。该体系使用二甲亚砜和乙二醇混合溶剂, 研究表明, 乙二醇能和氨水形成氢键阻止了氨从溶剂中逸出, 有利于氨的芳香化。
 | 图 11 CuSO4· 5H2O原位生成Cu+ 催化氨与卤代芳烃偶联Figure 11 Cu+ generated in situ for the coupling of ammonia and arylhalide |
在金属催化反应中, 催化剂与产物的分离、配体的合成成本等问题限制其在实际生产中的推广应用。开发出易分离和能循环使用的催化剂成为关注焦点。2011年, Xu H J等[34]制备的CuI纳米催化剂在温和条件下催化卤代芳烃生成苯胺、苯酚和噻酚等, 且经离心和过滤, 该催化剂可循环使用, 循环使用3次, 催化剂回收率82%, 苯胺产率80%。
 | 图 12 可循环CuI纳米催化氨与卤代芳烃偶联Figure 12 Recyclable CuI nanoparticles catalyzed coupling of ammonia and arylhalide |
2014年, Albadi J等[35]制备的负载型催化剂P4VPy-CuI在乙腈溶剂回流作用下, 实现卤代芳烃与氨水偶联, 催化剂循环使用3次, 偶联产率基本不变。Yang B等[36]开发的CuO/DTPA催化体系实现了水溶剂里催化卤代芳烃与氨偶联, 用水作溶剂, 通过有机相-水相萃取和分液, 将催化剂和产物分离, 实现催化剂的循环使用。
氨作为方便易得的原料, 在C-N偶联中成为研究焦点。经过近几十年的发展, 催化体系日益优化, 各种催化剂能高效催化该类反应。未来该类反应的发展方向应从以下方面解决:(1) 随着科技的发展, 环境问题日益受到关注, 开发绿色催化体系成为未来发展方向; (2) 能源问题是面临的重要问题, 在温和条件下(如室温)能高效催化的催化剂应是追求方向; (3) 需要开发更多的易分离且能循环使用的催化剂。到目前为止, 已有各种高效催化体系用于氨为氮源的C-N偶联反应, 但实际应用很少。因此, 该反应更重要的发展方向是在实际生产中的应用。
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|