作者简介:杨朋朋,1991年生,女,河南省商丘市人,硕士,主要从事环境功能材料的研究。
采用甲醛去除性能动态测试装置研究Mn/Fe物质的量比、水热温度、水热时间、焙烧温度、焙烧时间等工艺因素对锰铁氧化物催化剂室温甲醛去除性能的影响。采用X-射线衍射仪、扫描电子显微镜、能谱分析仪、透射电子显微镜、傅里叶变换红外光谱仪分析锰铁氧化物催化剂结构、形貌、微区成分、表面官能团等。结果表明,影响锰铁氧化物催化剂室温甲醛去除率强弱的顺序为:焙烧温度>煅烧时间>Mn/Fe物质的量比>水热时间>水热温度;催化剂的最佳制备工艺为:Mn/Fe物质的量比1.8:1,水热温度140 ℃,水热时间8.0 h,焙烧温度150 ℃时,焙烧时间4.5 h,该条件下制备催化剂的室温甲醛去除率为96.14%,经6次循环使用后活性仅下降5.06%;锰铁氧化物样品由MnO2、Fe2O3和非晶相组成,样品呈球形,平均粒径6.73 nm,表面官能团主要有O-H伸缩吸收、N-H弯曲振动、C-H弯曲振动等。
The effects of the technologic factors of mole ratio of iron to manganese,hydrothermal temperature and time,calcination temperature and time on the formaldehyde removal efficienvy at room temperature of manganese-iron oxides catalyst were investigated by using the dynamic test device for formaldehyde removal performance.The phase structure,morphology,micro area composition,surface functional groups of manganese-iron oxides were analyzed by using the X-ray diffraction,scanning electron microscope,energy spectrum analysis,transmission electron microscope,Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy.The results indicated that the sequence in terms of influence degree on the formaldehyde removal rate at room temperature of the manganese-iron oxides was calcination temperature,calcination time,mole ratio of iron to manganese,hydrothermal time and temperature.The optimal preparation technology of sample was that the mole ratio of iron to manganese was 1.8:1,and hydro-thermal synthesized at 140 ℃ for 8.0 h,then calcined at 150 ℃ for 4.5 h.The formaldehyde removal efficiency at room temperature of the sample prepared under the optimal conditions was 96.14% and only down 5.06% after six cycles.The manganese-iron oxides sample was composed of MnO2,Fe2O3 and amorphous phase,the particles of the specimen were spheroid whose average size was 6.73 nm,which contained the surface functional groups of O-H telescopic absorption,N-H bending vibration,C-H bending vibration.
近年来, 室内甲醛污染越来越严重并危及人类健康[1, 2], 去除甲醛主要有催化氧化[3]、光催化[4]、低温等离子[5]、吸附[6]等方法。其中, 催化氧化技术可将甲醛完全氧化为CO2、H2O, 是最具潜力的甲醛去除方法, 催化剂研究是该技术的关键, 主要包括过渡金属、贵金属、稀土金属(Mn、Co、Cu、Ag、Pt、Ce、Sr)等。过渡金属催化剂成本低、资源丰富, 具有良好稳定性[7]、耐受性[8, 9, 10]等, 且可通过掺杂贵金属或稀土金属提高表面积, 增加活性氧, 改善氧化还原性能[11, 12, 13]。
对于单一金属氧化物催化剂, 采用沉淀法制备的Co3O4颗粒[14]、纳米棒[15]的甲醛去除率分别为90%(反应温度225 ℃)、95%(反应温度120 ℃); MnO2三维有序介孔材料[16]在130 ℃时的甲醛去除率可达100%。复合金属氧化物催化剂方面, Cu-Mn氧化物[17]在(207~258) ℃时可将90 %的甲醛氧化为CO2和H2O; 采用共沉淀法、改性共沉淀法制备的Mn0.9Ce0.1O2、MnOx-CeO2催化剂[18, 19]在160 ℃、100 ℃时的甲醛去除率均可达100%。在负载贵金属研究方面, Ag/CeO2纳米颗粒[20]在200 ℃时的甲醛去除率达100%, 而Au/Fe2O3纳米材料[8]在室温条件下的甲醛去除率只有33%。尚未见到采用共沉淀法制备的过渡金属催化剂可在室温条件下完全降解甲醛的文献报道。
本文以室温去除甲醛为目的, 研究Mn/Fe物质的量比、水热温度、水热时间、焙烧温度、焙烧时间等因素对锰铁氧化物催化剂室温甲醛去除率的影响, 并采用XRD、SEM、TEM、EDX、FT-IR和Raman等方法表征样品的晶体结构、微观形貌、晶面、成分和表面官能团等。
按设定的Mn/Fe物质的量比称取高锰酸钾和硝酸铁, 置于200 mL烧杯中, 加入50 mL蒸馏水, 室温搅拌至完全溶解; 在持续搅拌的过程中缓慢滴加1 mol·L-1的沉淀剂碳酸钠溶液5 mL, 继续搅拌15 min; 滴加5 mol·L-1的氨水0.5 mL, 继续搅拌15 min; 置入水热反应釜中, 在一定温度下水热一定时间, 冷却; 用蒸馏水、无水乙醇清洗、离心3次; 经70 ℃保温10 h; 在一定温度下焙烧一定时间, 即可得到实验所需的锰铁氧化物催化剂样品。
采用D/Max-3c X-射线衍射仪分析样品的晶体结构, 扫描范围10° ~80° , 扫描速率为8° ·min-1。
采用FEI Quanta 200扫描电子显微镜对样品的微观形貌进行表征, 工作电压20 kV, 最大电流为80 nA, 真空度(2.8~3.6)× 10-3 Pa。
使用FEI型透射电子显微镜分析样品的晶面和晶格间距, 工作电压200 kV。
利用Spectrum Two傅里叶变换红外光谱仪分析样品表面官能团, 测试范围(4 000~400) cm-1。
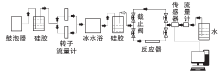
采用动态装置测试锰铁氧化物催化剂的室温甲醛去除性能, 如图1所示, 该装置主要包括气体发生装置、反应装置、测试装置、尾气处理。1)称取0.1 g催化剂样品放入三孔玻璃管中; 2)插上鼓泡器电源, 打开上路气体阀门, 调节气体流量计, 将甲醛、空气的流量控制为约0.1 L·min-1, 甲醛浓度约1.1 mg·m-3; 3)将称好的催化剂样品置入反应装置中, 关闭上路气体阀门, 打开下路气体阀门, 检测、记录甲醛浓度。
经前期初步研究, 选择Mn/Fe物质的量比(A)、水热温度(B)、水热时间(C)、焙烧时间(D)、焙烧温度(E)等为研究对象, 采用5因素4水平, 即L16(45)正交试验优化锰铁氧化物制备工艺条件, L16(45)正交试验因素与水平如表1所示, 正交试验设计及结果如表2所示。由表2可知, 采用水热沉淀法制备锰铁氧化物催化剂的最佳工艺为:Mn/Fe物质的量比为1.8:1、水热温度为140 ℃、水热时间为7.5 h、焙烧温度为150 ℃、焙烧时间为5.0 h, 该工艺条件下制备的锰铁催化剂样品室温甲醛去除率为95.86%。
| 表1 L16(45)正交试验因素与水平 Table 1 Factors and levels of L16(45) orthogonal experimental |
| 表2 正交试验设计及结果 Table 2 Design and results of orthogonal experimental |
为了得出工艺因素对样品室温甲醛去除率的影响程度, 计算每个因素各个水平的室温甲醛去除率的总和, 取算术平均数, 得出极差, 结果如表3所示。
| 表3 锰铁氧化物室温甲醛去除率的极差分析 Table 3 Range analysis of formaldehyde removal efficiency of manganese-iron oxide at room temperature |
由表3可知, 所研究的5个工艺因素对锰铁氧化物催化剂样品室温甲醛去除率的影响都比较大, 其中, 焙烧温度的影响最大, 水热温度的影响最小; 影响锰铁氧化物室温甲醛去除率强弱的顺序依次为:焙烧温度> Mn/Fe物质的量比> 焙烧时间> 水热时间> 水热温度; 由表3还可以得出, 水热沉淀法制备锰铁氧化物的最佳优化工艺为A2B4C4D1E1, 即Mn/Fe物质的量比1.8:1, 水热温度140 ℃, 水热时间8.0 h, 焙烧温度150 ℃, 焙烧时间4.5 h时, 该工艺条件下制备的催化剂样品室温甲醛去除率为96.14%。
表4为最优工艺条件下制备的锰铁氧化物催化剂经6次循环使用的室温甲醛去除结果。由表4可知, 随着循环使用次数的增加, 锰铁氧化物催化剂的室温甲醛去除率逐渐降低, 经6次循环后, 样品的甲醛去除率由96.14%减少到91.08%, 仅下降了5.06%, 表明锰铁氧化物催化剂具有良好的催化氧化甲醛稳定性。
| 表4 锰铁氧化物循环使用的室温甲醛去除率 Table 4 Formaldehyde removal efficiency of manganese-iron oxide recycling at room temperature |
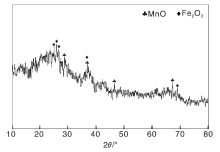
最佳工艺条件下制备的锰铁氧化物催化剂XRD图如图2所示。由图2可以看出, 锰铁氧化物催化剂由非晶相和MnO2、Fe2O3晶体相组成, 没有其它杂质的衍射峰。
最佳工艺条件下制备的锰铁氧化物催化剂SEM照片、TEM照片及分析结果如图3所示, 微区成分分析结果如表5所示。由图3和表5可知, 锰铁氧化物催化剂的微观形貌呈球形或近球形, 主要是由于共沉淀法制备样品所致[21], 颗粒直径范围约为(2.0~9.2) nm, 平均粒径为6.73 nm, 微区成分为ω (Mn)=42.89%、ω (Fe)=27.39%Fe、ω (O)=29.72%; 从图3还可以看出, 锰铁氧化物催化剂暴露的晶面为(104)、(310), 晶格间距分别为0.27 nm、0.30 nm。
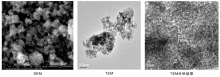 | 图3 锰铁氧化物样品的SEM照片、TEM照片及分析结果Figure 3 SEM and TEM images and TEM analysis result of manganese-iron oxide catalyst |
| 表5 锰铁氧化物催化剂EDX分析结果 Table 5 EDX analysis of manganese-iron oxide catalyst |
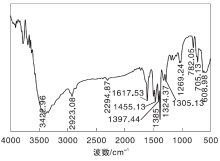
最佳工艺条件下制备的锰铁氧化物催化剂FT-IR谱图如图4所示。从图4可以看出, 锰铁氧化物催化剂在3 422.5 cm-1、2 923.08 cm-1、2 294.87 cm-1、1 617.53 cm-1、1 455.13 cm-1、1 397.44 cm-1、1 385.00 cm-1处有明显的特征峰, 分别对应饱和C-H伸缩振动、C-H伸缩振动、O-H伸缩吸收、C-H弯曲振动、N-H弯曲振动、C=C骨架振动、C-H弯曲振动。
(1) 影响锰铁氧化物催化剂室温甲醛去除率强弱的顺序为:焙烧温度> Mn/Fe物质的量比> 焙烧时间> 水热时间> 水热温度。
(2)锰铁氧化物催化剂最佳制备工艺条件为Mn/Fe物质的量比1.8:1, 水热温度140 ℃, 水热时间8.0 h, 焙烧时间4.5 h, 焙烧温度150 ℃时, 最佳条件下制备样品的室温甲醛去除率为96.14%, 经6次循环使用后, 甲醛去除率仅下降5.06%, 具有良好的催化氧化活性。
(3) 锰铁氧化物催化剂由非晶相和MnO2、
(4) 催化剂样品在室温条件下甲醛去除率未能达到100%, 为了能在室温条件完全氧化甲醛, 下一步将在本实验的基础上掺杂贵金属或稀土元素, 探索室温条件下的甲醛去除率。
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|